Parapet wall detail plan and elevation layout file Cadbull

Architectural Details
Design guide for parapets: Safety, continuity, and the building code. The modern parapet must provide fire protection, serve as a fall-protective guard, transition and protect the roof/facade interface, conceal rooftop equipment, and contribute to the aesthetic character of the building. course credit: 1.0 AIA LU/HSW, 1.0 PDH Provided By: BD+C.

Moisture Management of Parapet Walls Masonry Technology, Inc.
A parapet wall is constructed on the edge of the roof. You should know about the requirements and the dimensions for a parapet wall design

Moisture Management of Parapet Walls Masonry Technology, Inc.
The easiest thing to get right about parapet construction is to keep rainwater from getting into the top of them. The principles are easy. Slope the top of them inward so they don't stain the building façade. Make sure that there is a waterproof membrane under the coping. Always. Metal and stone copings leak at joints.

Image result for timber parapet wall detail Parapet, Roof detail, Roof
The parapet is a minor wall around the edge of a roof, balcony, terrace, or stairway, usually covering the roof's perimeter. It protects the top and pre-built structures from corrosion and degradation. The Functions Of The Parapet Wall: Blowing wind creates a vortex on the edges of the roof and causes a gigantic pressure difference.

Parapet detail at masonry wall.
Parapet Wall Roofing Guide (Exterior Design Types + Construction Details) If you are looking for a quick parapet definition, skip ahead to the first section. Otherwise, choose the table of contents menu below for navigation to the parapet roof section you're most interested in. Table of Contents [ hide] What Is A Parapet? History of Parapets

Parapet Wall Detail Sketch Parapet, Roof detail, Roof work
Blog Post. Parapet walls behave differently to conventional cavity walls because of their location at the very top of a building where both skins of the parapet are outer skins, and as such are exposed to moisture. Traditionally constructed parapet walls can become saturated with rain and are also subject to extremes of heat and cold, leading.

Image result for parapet wall Membrane, Cladding, The Professional
There are 2 options for building parapet walls: Standard - where the AB Dogbones connect the facing units together. Easily build corners and parapets with posts. Offers the smallest width, for straight walls only. Wider - where the AB Dogbones act as anchors in the wall rock allowing any size width to be created.

Typical parapet wall detail Parapet, Architecture details, Flat roof
🕑 Reading time: 1 minute A parapet wall is a low or dwarf wall built along the edge of the roof, terrace, walkway, balcony etc. Parapet walls can be constructed using different materials like reinforced cement concrete, steel, aluminium, glass etc. Different types of parapet walls and their uses are discussed below. Types of Parapet […]

Parapet wall sectional detail dwg file Cadbull
Parapet Wall Design Brian Erickson, P.E., RRC Ryan Krug - 8:30 am - 10:00 am NOVEMBER 14, 2017 Brian D. Erickson, P.E., RRC Vice President - Midwest, Pie Consulting & Engineering Licensed PE in 6 states Registered Roof Consultant Iowa State University and University of Colorado 3rd Speaking Opportunity at AIA MN! Ryan Krug, BECxP, CxA+BE

concrete parapet wall detail Google Search Gypsum Wall, Architecture
Characterized as a low wall, the parapet projects above the roof plane and typically spans around the perimeter of the roof area. Histori-cally, parapets were constructed of masonry, consisting of multi-wythe walls with mortar-fi lled collar joints, capped with a coping.

Water intrusion consultations for wet and leaking buildings Decker
A demonstration of assembling a parapet wall detail using a combination of profiles and composites. Enjoy!!!🟠Project Files; https://tinyurl.com/mxk6bvs6🔵Ar.

Remediation details parapets BRANZ Weathertight
Some of the more common ways I have seen the ends of copings detailed include the following: 1) the coping terminates horizontally at or near the surface of the wall cladding; 2) the coping extends into the wall cladding (for example, masonry or EIFS) without an upturned leg and integral side flanges; and 3) the coping terminates within the wall.

Moisture Management of Parapet Walls Masonry Technology, Inc.
DESCRIBE the design of parapet components, including copings, cladding, sealants, mortar joints, in-wall flashings, and vapor barriers, and explain how each functions to protect wall and roof assemblies from water infiltration. DISCUSS the impact of code requirements for energy performance (e.g., the International Energy Conservation Code) on.

How to get it right Parapet walls LABC
of precise details can promote the longevity of a parapet and prevent common issues like freeze/ thaw deteriora-tion from arising. The goal is to di-minish the impact of moisture on the wall assem-bly by redirecting water away from the building. Copings. The first line of defense for a . parapet is the coping. Somewhat larger than the width of.
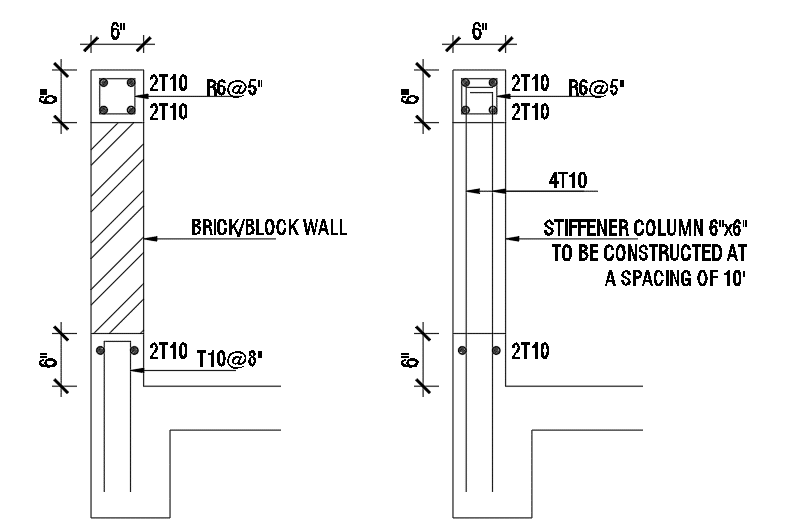
Parapet Walls Types, Uses and Construction Structural Guide
Coping - Construction that protects the top of a wall, balustrade, or parapet and sheds rainwater clear of the surfaces beneath. Capping - Construction that protects the top of a wall, but does not shed rainwater clear of the surfaces of the wall beneath.

TYPICAL PARAPET DETAIL a photo on Flickriver
1. Height of roofing at wall: minimum of 12" to top of parapet. Do not lap TPO over top of parapet unless required by unique construction conditions. 2. Top of parapet, below cap, to be sealed with fluid applied flashing. 3. Venting in wood framed parapets: Provide venting to each wall cavity.