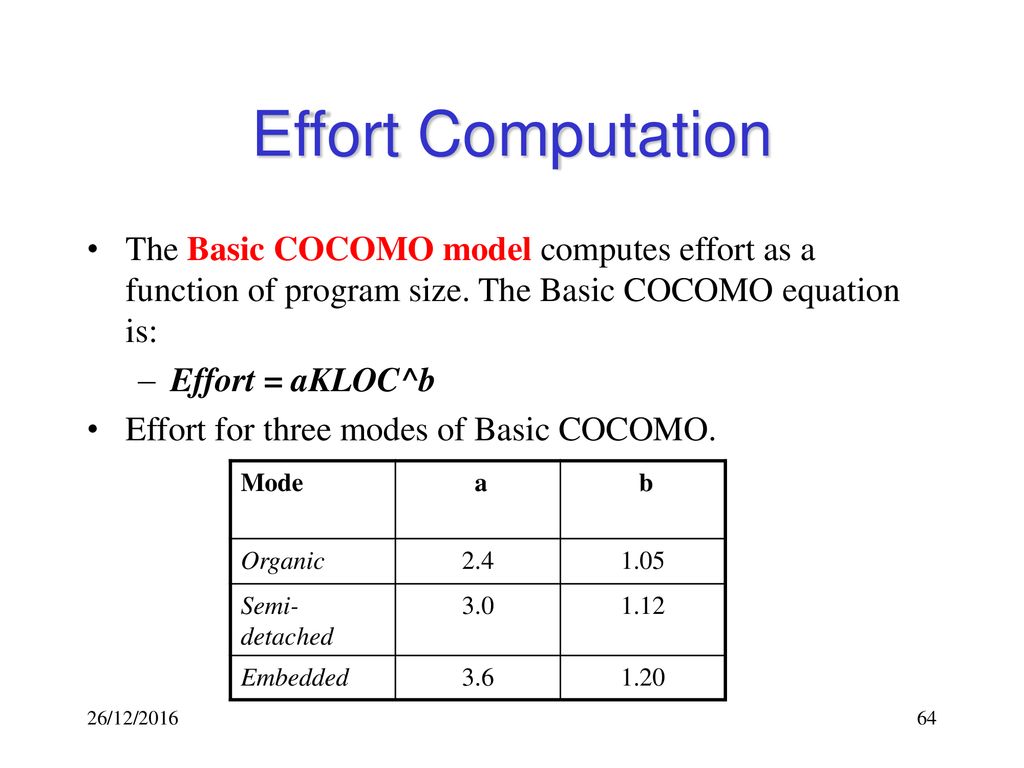
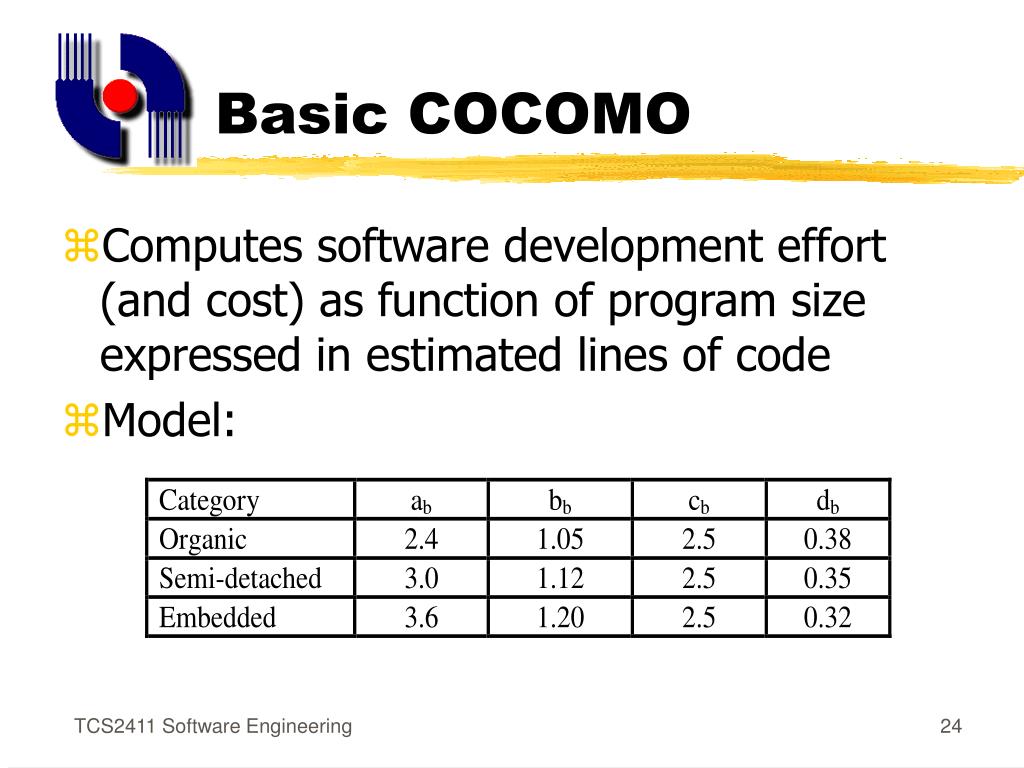
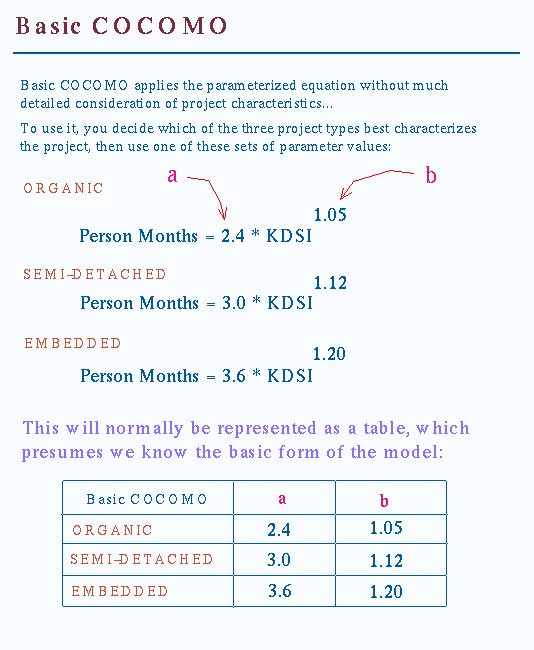
Difference between basic model and intermediate model and complete model

L26 II Application Composition Estimation Effort Estimation Steps Software
COCOMO-II is the revised version of the original Cocomo (Constructive Cost Model) and was developed at the University of Southern California. It is the model that allows one to estimate the cost, effort, and schedule when planning a new software development activity. Sub-Models of COCOMO Model COCOMO Sub-models 1. End User Programming
Basic Mmodel Program In C ortholasopa
COCOMO (COnstructive COst MOdel II) Launch Tool Last Updated : 03/27/2017 A model that facilitates estimation of cost, effort and schedule when planning a new software development activity. Originally established 1981, it includes three sub-models each offering further fidelity, called Applications Composition, Early Design, and Post-Architecture.

II YouTube
Effort Is the effort from the COCOMO II effort equation SE Is the schedule equation exponent derived from the five Scale Drivers Continuing the example, and substituting the exponent of 0.3179 that is calculated from the scale drivers, yields an estimate of just over a year, and an average staffing of between 3 and 4 people:
PPT Software Cost Estimation PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID294384
Basic COCOMO Model. The purpose of this site is to help the end user making an estimate using the COCOMO model (s). The end user will be able to use one (1) of the three (3) models, which is the. In his classic book on "Software Enginnering Econonics," Barry Boehm introduces a hierarchy of software estimation models bearing the name . Boehm's.

PPT VoiceXML Basic Calculator PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9690612
CO nstructive CO st MO del II (COCOMO ® II) is a model that allows one to estimate the cost, effort, and schedule when planning a new software development activity. COCOMO II is the latest major extension to the original COCOMO model published in 1981 (now referred to as COCOMO 81 ).

Table 1 from Optimization of II Effort Estimation using Algorithm Semantic Scholar
It is used at the Stage - II in COCOMO -II models and supports estimation in early design stage of project. Base equation used in COCOMO - II models is as follows -. PM nominal = A * (size) B where PM nominal = Effort for the project in person months A = constant representing the nominal productivity where A = 2.5 B = Scale Factor Size = size of the Software

model calculator masagun
COCOMO II - Constructive Cost Model Software Size Sizing Method Software Scale Drivers Maintenance Software Labor Rates Cost per Person-Month (Dollars) Results Software Development (Elaboration and Construction) Effort = 0.0 Person-months Schedule = 0.0 Months Cost = $0 Total Equivalent Size = 0 SLOC Effort Adjustment Factor (EAF) = 1.00

Difference between basic model and intermediate model and complete model
COCOMO II suggests calibration to the specific organization in order to achieve the most accurate results. It supports two types of calibrations where the most comprehensive calibration has not been made because of the large effort needed to gather project data. As the goal is to develop a meta model that enables software change estimation for.

II
Basic COCOMO Calculator (Baker) Basic COCOMO Calculator (Kutcher) Basic COCOMO Calculator (Mohamed & Fouani)

Model Calculator Tool Tech Yatri
The Constructive Cost Model (COCOMO) computation is used to estimate the level of effort needed to produce a given quantity of code. The project should save the results of this COCOMO calculation if needed to support its make or buy decision. Form to submit Constructive Cost Model (COCOMO) calculation.

SOLUTION model Studypool
COCOMO II has 17 cost drivers - you assess your project, development environment, and team to set each cost driver. The cost drivers are multiplicative factors that determine the effort required to complete your software project. For example, if your project will develop software that controls an airplane's flight, you would set the Required.

Cost estimation using model example taiahh
COCOMO is the world's most widely used software estimation model. Software project managers use SystemStar to produce estimates of a project's duration, staffing levels, effort, and cost. SystemStar lets you make trade-offs and experiment with "what-if" analyses to arrive at the optimal project plan.
nebud lol víťaz calculator vzdialenosť premena dutý
The Little COCOMO Calculator by Dr. Brad Clark (Software Metrics Inc.) and Dr. Ray Madachy (Naval Post Graduate School) COCOMO II The updated COCOMO 81 model published in 2000. It predicts software development effort, schedule, and effort distribution via range estimates. COCOMO II Web Tool by Dr. Ray Madachy (Naval Postgraduate School) COCOMO III

Software Cost Estimation with II
COCOMO II is really three different models: The Application Composition Model Suitable for projects built with modern GUI-builder tools. Based on new Object Points. The Early Design Model You can use this model to get rough estimates of a project's cost and duration before you've determined it's entire architecture.

Table 2 from The Rosetta Stone Making 81 Estimates Work with II Semantic Scholar
This article provides a sample of COCOMO II cost estimate for a real project, and concentrates on outlining basic how-to when project manager needs some advice on making simple cost estimates and tools that can be used. Audience
GitHub React site for basic and Intermediate calculation
Constructive Cost Model II (COCOMO II Model) create large extent most considerable and broadly used as model for cost estimation. To estimate the effort and the development time of a software project, COCOMO II model uses cost drivers, scale factors and line of code. However, the model is still lacking in terms of accuracy both in effort and.