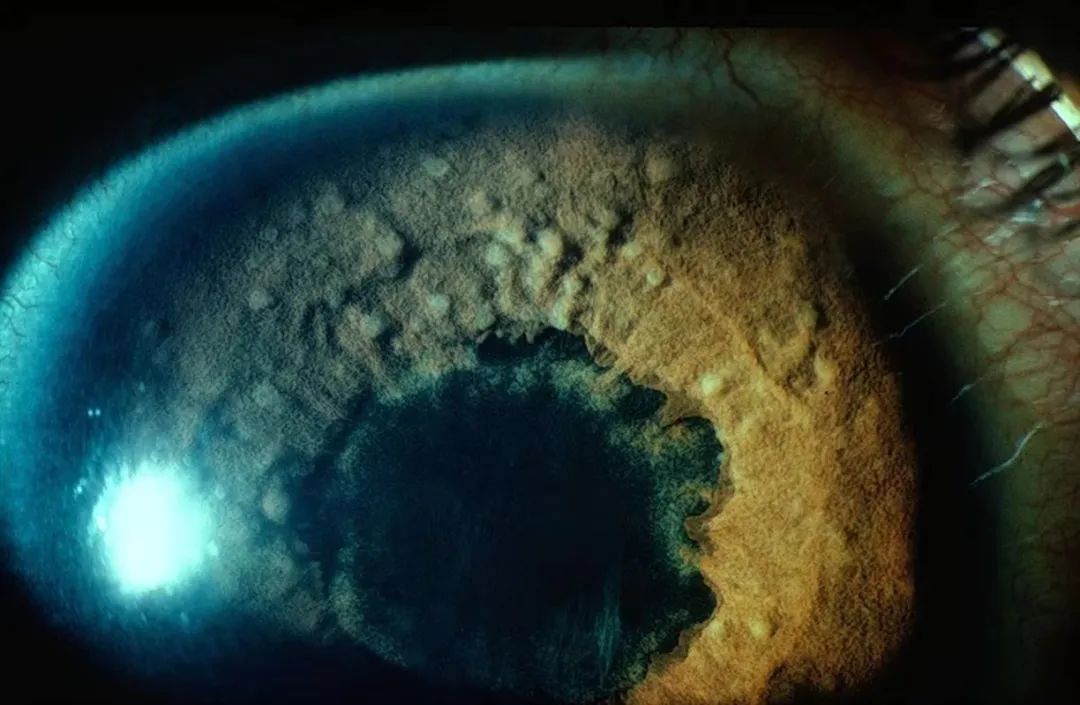
Pupil margin (Koeppe) and iris surface (Busacca) nodules in a patient

Panuveitis
Iris nodules (Koeppe/Busacca) [Figures 5a and. Two types of iris nodules can develop in granulomatous uveitis. When situated at the pupillary margin (and on the surface of the iris) they are called Koeppe nodules, have a fluffy appearance and a size going from very small barely visible excresences to frank nodules. When situated in the body.

Iris nodules in Fuchs heterochromic iridocyclitis. Abstract Europe PMC
Background/aim: Iris nodules are an uncommon clinical sign in uveitis. The diseases most commonly associated with iris nodules and uveitis include sarcoidosis, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome, multiple sclerosis, Fuchs' heterochromic iridocyclitis, and metastatic infection. While many of these diseases may be appropriately treated with immunosuppressive medication, the management of infectious.
Iris nodules neurofibromatosis American Academy of Ophthalmology
The Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature (SUN) Working Group classifies onset as either "sudden," which is characterized by pain, redness and photophobia, or "insidious," where the eye is painless and white.2 • Duration.
Koeppe nodules American Academy of Ophthalmology
The diseases most commonly associated with iris nodules and uveitis include sarcoidosis, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome, multiple sclerosis, Fuchs' heterochromic iridocyclitis, and metastatic infection.

NODULES in Ophthalmology
Iritis, also known as anterior uveitis, is the most common form of intra-ocular inflammation and often causes a painful red eye. The term uveitis is synonymous with inflammation of the uveal tract,.

Iris nodules ️Koeppe... OphthalmologyNotes And Synopses Facebook
Sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory disease of unknown etiology characterized by the formation of noncaseating granulomas. The disease most commonly affects the skin, lungs, lymph nodes, and eyes but can affect virtually any organ.

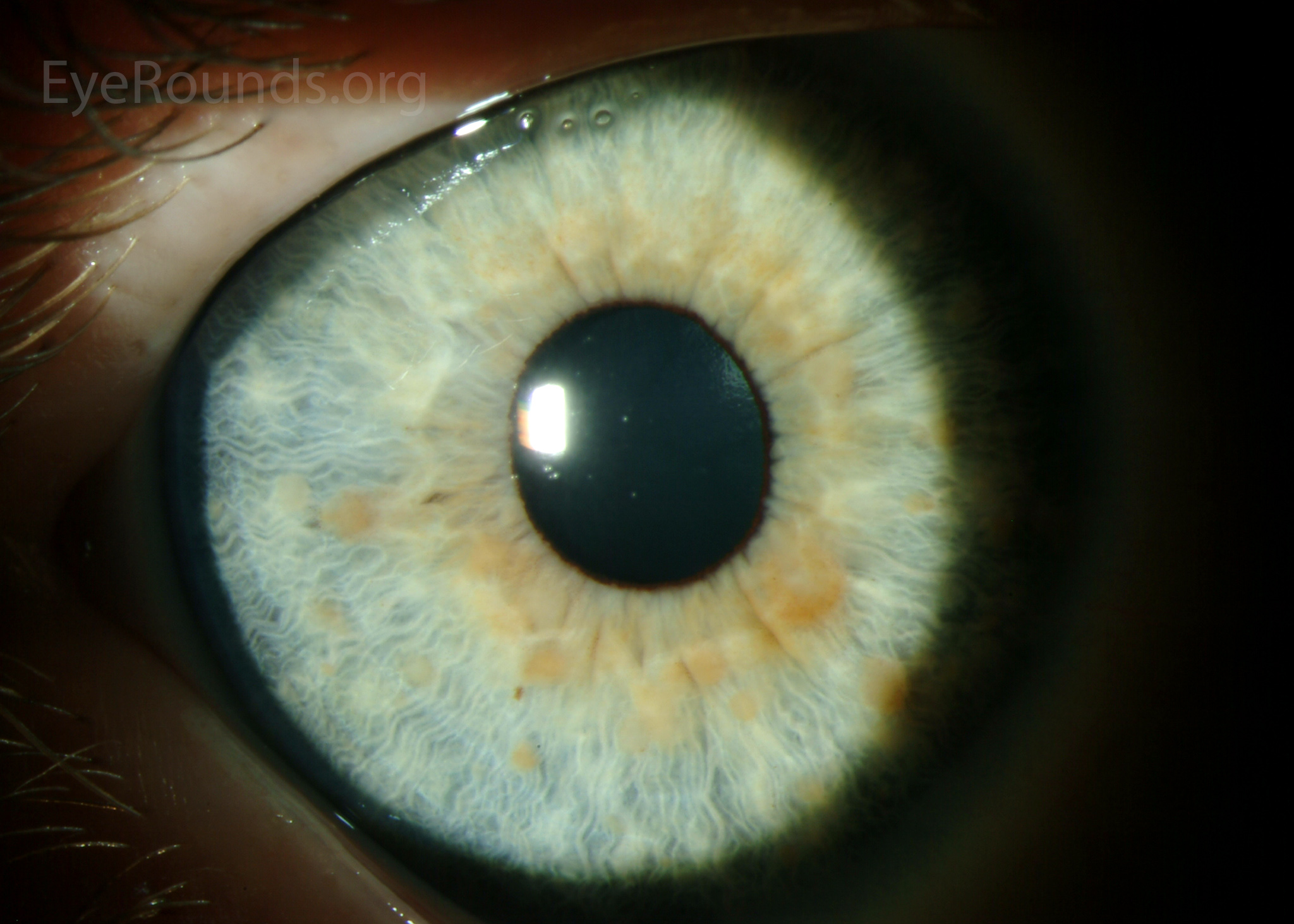
FHU affecting the right eye with mild heterochromia. Both Koeppe (pupil
Koeppe's nodules are small nodules seen at the inner margin of the iris in patients with granulomatous anterior uveitis, which occurs in conditions such as sarcoidosis and tuberculosis. The nodules are composed of epithelioid cells and giant cells surrounded by lymphocytes.
Koeppe nodules and muttonfat keratic precipitates American Academy
Nodules found at the pupillary border are known as Koeppe nodules and those found on the surface of the iris are referred to as Busaca nodules. 7. FUS is a clinical diagnosis, dependent on the eye examination. To detect the presence of rubella-specific antibodies, an anterior chamber paracentesis may be completed, however, this is not a.

Üveit Nedir? Nasıl Bir Hastalıktır? • Doktordan Haberler
Objectives: Describe the pathogenesis of ocular sarcoidosis. Summarize the relevant history of patients with ocular sarcoidosis. Review the evaluation process of patients with ocular sarcoidosis. Outline the management of ocular sarcoidosis, including the role of interprofessional care of these patients.
肉芽肿性炎和非肉芽肿性炎有何区别?4个结节要分清_医学界助力医生临床决策和职业成长
Koeppe's nodules are small nodules seen at the inner margin of the iris in patients with granulomatous anterior uveitis, which occurs in conditions such as sarcoidosis and tuberculosis. [1] The nodules are composed of epithelioid cells and giant cells surrounded by lymphocytes. [2] Koeppe's nodules are named after Leonhard Koeppe . References

Opthalmic Technician, Optician Training, Optometry School, Eye Facts
Koeppe Nodules Koeppe's nodules are small nodules seen at the inner margin of the iris in patients with granulomatous anterior uveitis, which occurs in conditions sich as sarcoidosis and tuberculosis.

Pupil margin (Koeppe) and iris surface (Busacca) nodules in a patient
In comparison, smaller koeppe nodules located on the pupillary border may be seen in both granulomatous and nongranulomatous irides. 7,8 Posterior segment involvement occurs in approximately one third of patients with ocular sarcoidosis, and typically presents as an intermediate uveitis. 3,7,8 Peripheral neovascularization, with or without.
Atlas Entry Lisch nodules
Definition A type of iris nodule consisting of inflammatory cell precipitates which lie at the pupillary margin. [from HPO] Term Hierarchy GTR MeSH CClinical test, RResearch test, OOMIM, GGeneReviews, VClinVar CROGVKoeppe nodules Phenotypic abnormality Abnormality of the eye Abnormal eye morphology Iris nodule Koeppe nodules Professional guidelines
Atlas Entry Sarcoidosis
Viral anterior uveitis (VAU) is characterized by anterior uveitis (AU) with elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) diffuse stellate keratic precipitates (KPs), presence of pigmentation in active KPs and iris atrophic changes. [ 1 2 3 4] The most commonly implicated viruses include herpes simplex (HSV), varicella-zoster (VZV), cytomegalovirus (CMV),.

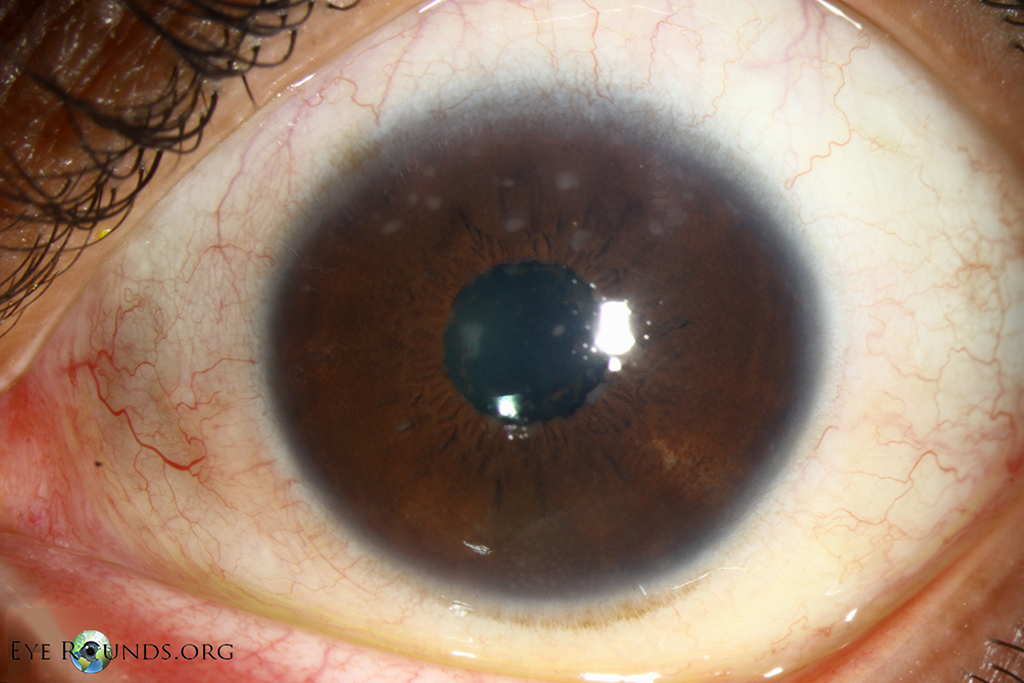
Multiple Koeppe nodules (white arrows) at iris pupillary border noted
Koeppe's Nodules May be found as: Koeppe nodules (inflammatory cell precipitates which lie at the pupillary margin and could be found in non-granulomaous as well as granulomatous uveitis) Bussaca nodules (lie on the iris surface) which are pathognomonic for granulomatous uveitis. When the inflammation is treated, the nodules will resolve.

lisch nodules Google Search NF 1 Анатомия человека, Искусство глаза
Other features of granulomatous anterior uveitis include presence of Koeppe's nodules at the pupillary border and/or Busacca's nodules in the iris stroma.