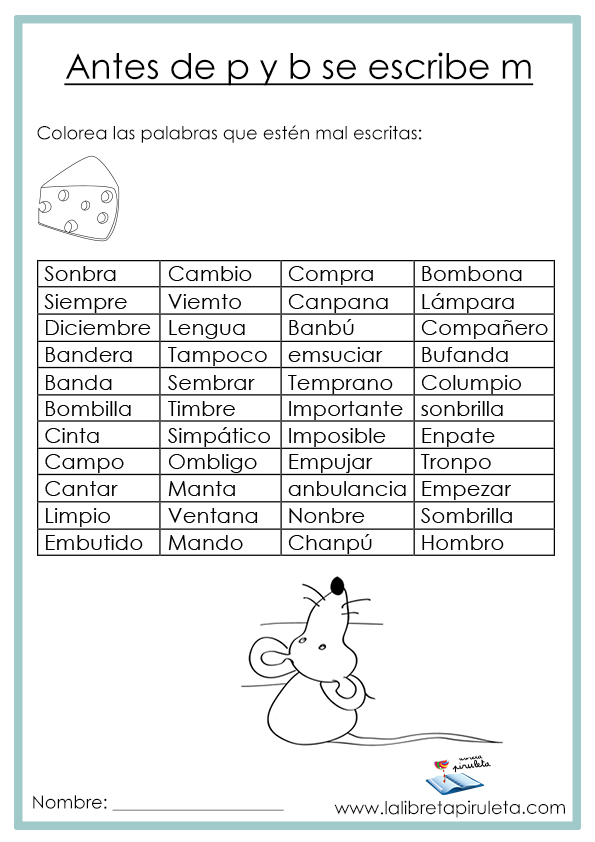
M antes de P y B ficha interactiva y descargable. Puedes hacer los ejercicios online o des

Pin en Educacion Denis
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\) For an example of conditional distributions for discrete random variables, we return to the context of Example 5.1.1, where the underlying probability experiment was to flip a fair coin three times, and the random variable \(X\) denoted the number of heads obtained and the random variable \(Y\) denoted the winnings when betting on the placement of the first heads.

M antes de p y b
Classic Country WPYB. Johnston and Harnett Counties home for the best in Country Classics. Streaming 24 Hours a day!

Uso de la m antes de p y b
It may now be shown that P(X ∈ A,Y ∈ B) = P(X ∈ A)P(Y ∈ B) for any sets A ⊂ R and B ⊂ R. Thus X and Y are independent. The following result for jointly continuous random variables now follows. Theorem 15.3. Suppose X and Y are jointly continuous random variables
LES GUINEUS Castellano
It is computed using the formula μ = ∑ xP(x) μ = ∑ x P ( x). The variance σ2 σ 2 and standard deviation σ σ of a discrete random variable X X are numbers that indicate the variability of X X over numerous trials of the experiment. They may be computed using the formula σ2 = [∑x2P(x)] −μ2 σ 2 = [ ∑ x 2 P ( x)] − μ 2.

Uso de "m" antes de "p" y "b" Lenguaje Segundo Grado YouTube
E[XjBn]P(Bn) Now suppose that X and Y are discrete RV's. If y is in the range of Y then Y = y is a event with nonzero probability, so we can use it as the B in the above. So f(xjY = y) is de ned. We can change the notation to make it look like the continuous case and write f(xjY = y) as fXjY (xjy). Of course it is given by fXjY (xjy) = P(X.

Uso de la m antes de p y b
Note that conditions #1 and #2 in Definition 5.1.1 are required for to be a valid joint pmf, while the third condition tells us how to use the joint pmf to find probabilities for the pair of random variables . In the discrete case, we can obtain the joint cumulative distribution function (joint cdf) of and by summing the joint pmf:

H A P P Y B O Y E aww
p X(a)=P(X =a)=å y P X;Y(a;y) p Y(b)=P(Y =b)=å x P X;Y(x;b) In the continuous case a joint probability density function tells you the relative probability of any combination of events X =a and Y =y. In the discrete case, we can define the function p X;Y non-parametrically. Instead of using a formula for p we

Érase una vez Palabras con "m" antes de "p" y "b"
YouTube's Official Channel helps you discover what's new & trending globally. Watch must-see videos, from music to culture to Internet phenomena

barrialblogdeclase La m delante de p y b
P(Y|B) reads 'Probability of event Y happening given event B is happening'. This is a conditional probability and the formula is given as P(Y|B) = P(Y∩B) / P(B)

Las palabras con br, bl, mp, mb
v. t. e. Given two random variables that are defined on the same probability space, [1] the joint probability distribution is the corresponding probability distribution on all possible pairs of outputs. The joint distribution can just as well be considered for any given number of random variables. The joint distribution encodes the marginal.

EL BLOG DE TERCERO LA M ANTES DE P Y B
Are the events independent? Case 1: G G happens When the first marble drawn is green, there are 7 7 marbles left in the bag, and 5 5 of them are blue. In this case, P (B)=\dfrac {5} {7} P (B) = 75.

an image of the spanish words in front of mountains and hills with trees on them
Earlier Report - Daughter Searches For Answers 10 Years After Father's Murder In Mamaroneck; During the episode, listeners will get to hear from the case detective currently leading the investigation into the murder, Lt. P.J. Trujillo, as well as one of the original investigators at the scene of the incident.

Fichas de ORTOGRAFÍA M antes de P y B La libreta piruleta Learning Spanish For Kids, Spanish
Expert Math Tutor About this tutor › Let y denote a geometric random variable with probability function p (y)=p* (q)^ (y-1) y=1,2,3,. o<=p<=1 , q = 1-p Show that 1)for a positive integer a , P (Y>a)= q^a The easiest way for me with a problem like this is first to find the complement of P (Y>a), which is P (Y ≤ a), and subtract it from 1.

EL BLOG DE TERCERO LA M ANTES DE P Y B
Let's work some examples to make the notion of variance clear. Example 1. Compute the mean, variance and standard deviation of the random variable. X with the following table of values and probabilities. value x 1 3 5. pmf p(x) 1/4 1/4 1/2. answer: First we compute E(X) = 7/2. Then we extend the table to include (X − 7/2)2 .

H A P P Y B I R T H D A Y ♪♫•*¨*•.¸¸♫♪ KPop _ Amino
P (X;Y ) (A B) = P X (A)P Y (B) for all measurable subsets AˆSand BˆT. That is, Xand Y are independent if the joint distribution P (X;Y ) is the product of the measures P X and P Y. We use this criterion to prove the following theorem: Proposition 2 Expectation of a Product Let X;Y:

las palabras con m antes de p y de b YouTube
The joint probability mass function of two discrete random variables X X and Y Y is defined as PXY(x, y) = P(X = x, Y = y). P X Y ( x, y) = P ( X = x, Y = y). Note that as usual, the comma means "and," so we can write PXY(x, y) = P(X = x, Y = y) = P((X = x) and (Y = y)). P X Y ( x, y) = P ( X = x, Y = y) = P ( ( X = x) and ( Y = y)).