Gravitation Erklärung, Newton’s Gravitationsgesetz, Berechnung (Physik) YouTube
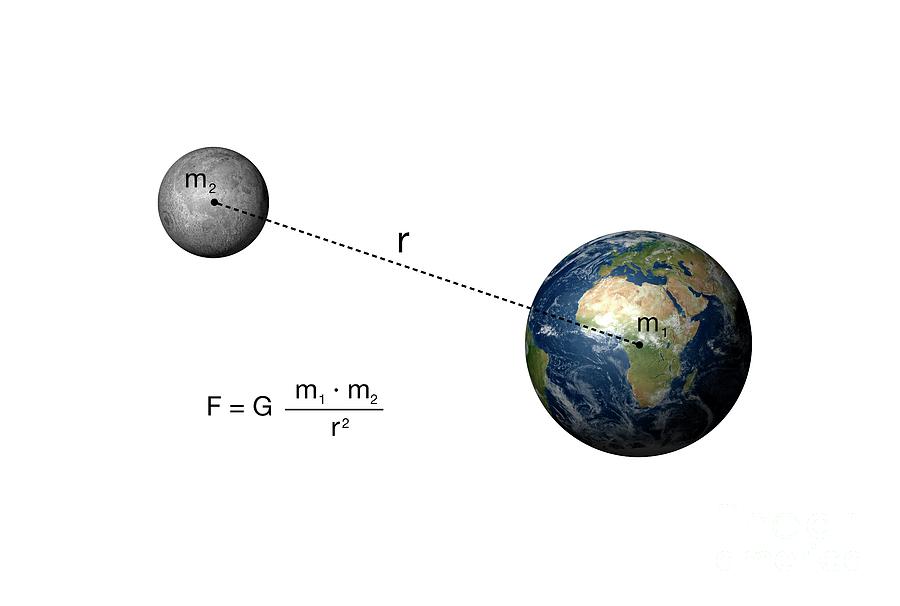
Newton's Law Of Gravitation And The Earthmoon System 2 Photograph by Mikkel Juul Jensen
Das Gravitationsgesetz gilt als eine der Grundlagen für die klassische Mechanik. Die Größe der Gravitationskraft ist abhängig von der Masse der Körper und der Distanz beider Massepunkte. Die von Newton aufgestellte Formel für die Gravitationskraft lautet: F G = G ⋅ m 1 ⋅ m 2 r 2.

Gravitationsgesetz • Newtonsches Gravitationsgesetz · [mit Video]
Abstract: This article examines the development of the law of gravitation in the writings of Isaac Newton, Immanuel Kant and Jakob Friedrich Fries. Fries was a philosopher, mathematician and physicist who stood in the Kantian tradition, but who nevertheless had empiricist leanings.. Görg, Erdmann. "Zum Gravitationsgesetz bei Newton, Kant.
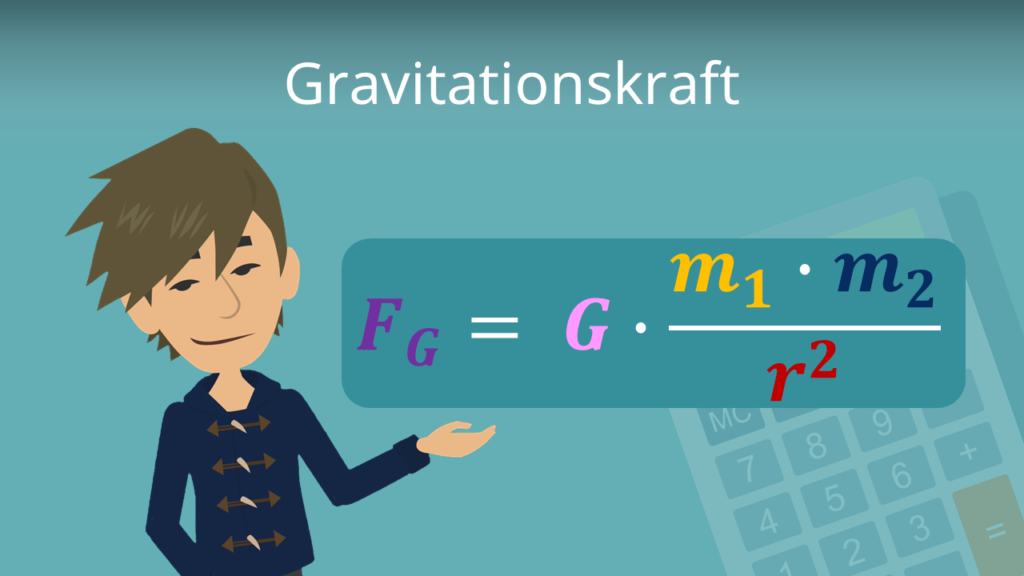
Gravitationsgesetz • Newtonsches Gravitationsgesetz · [mit Video]
Abb. 1 Isaac NEWTON (1643 - 1727) Neben den drei von ihm formulierten Axiomen (Trägheitssatz, Kraftgesetz und Wechselwirkungsgesetz) dürfte das Gravitationsgesetz, welches die Kraftwirkung zwischen zwei Körpern beschreibt, eine der wichtigsten Errungenschaften sein, die wir dem Genie Isaac NEWTON (1643 - 1727) zu verdanken haben. Angeblich soll NEWTON die Idee zum Gravitationsgesetz.

Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation YouTube
A genius with dark secrets. Isaac Newton changed the way we understand the Universe. Revered in his own lifetime, he discovered the laws of gravity and motion and invented calculus. He helped to.

Newtonsches Gravitationsgesetz YouTube
Isaac Newton: einfach erklärt Erfindungen, Steckbrief, Lebenslauf Newton Isaac Schwerkraft mit kostenlosem Video. So entdeckte Isaac Newton die Schwerkraft und entwickelte das Gravitationsgesetz. Außerdem beschäftigte sich der britische Wissenschaftler mit der Optik.

PPT Gravitationswellen PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4439023
Isaac Newton als Namensgeber Die äquivalenten Anziehungskräfte zweier Massen Das Newtonsche Gravitationsgesetz ist ein Gesetz der klassischen Physik, nach dem jeder Massenpunkt auf jeden anderen Massenpunkt mit einer anziehenden Gravitationskraft einwirkt.

Gravitational Force Definition, Formula, Examples, Properties, FAQs
Gravitationsgesetz und -feld Ausblick. NEWTONs Herleitung des Gravitationsgesetzes. Vorlesen. Vorbemerkungen. Während KEPLER und seine Vorläufer sich im Wesentlichen damit beschäftigten, wie sich ein Planet bewegt, ist NEWTON aufgrund seiner Axiome als erster in der Lage auch die Frage "warum sich ein Planet gerade so bewegt" anzugehen.

Gravitation Erklärung, Newton’s Gravitationsgesetz, Berechnung (Physik) YouTube
This is a general physical law derived from empirical observations by what Isaac Newton called inductive reasoning. It is a part of classical mechanics and was formulated in Newton's work Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ("the Principia"), first published on 5 July 1687. The equation for universal gravitation thus takes the form:

Das Newtonsche Gravitationsgesetz (Physik10bcUER KW17a) YouTube
The story of the gravitational constant, Big G: In 1686 Isaac Newton realized that the motion of the planets and the moon as well as that of a falling apple could be explained by his Law of Universal Gravitation, which states that any two objects attract each other with a force equal to the product of their masses divided by the square of their separation times a constant of proportionality.

Что такое гравитация и как она работает, простыми словами РБК Тренды
Sir Isaac Newton's law of inertia states an object will continue to move in a straight line unless acted on by another force. But then, how did this explain why the moon orbited the earth? What was the other force? Newton theorized the same force that caused an apple to fall from a tree was also the force that kept the moon in place. Over several years, Newton worked until he had developed.
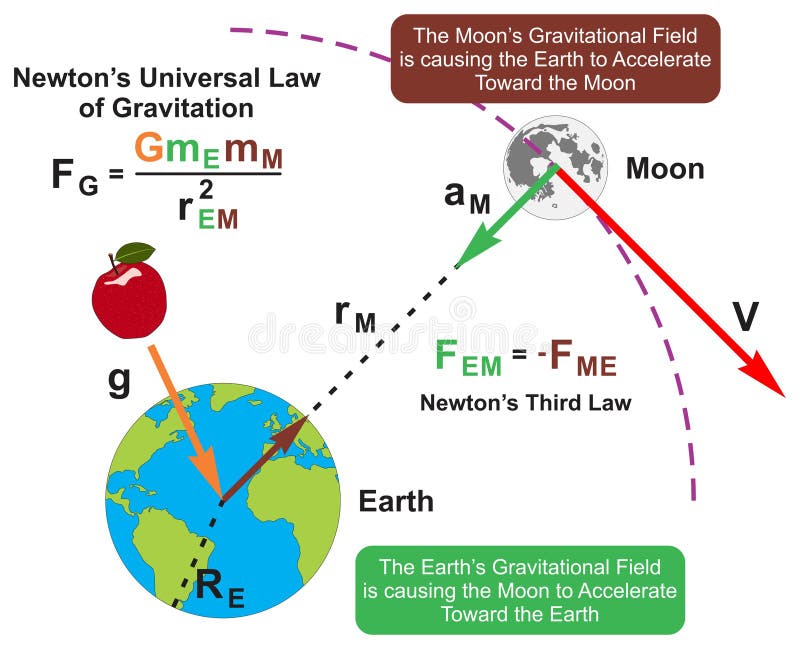
Newton Universal Law of Gravitation Infographic Diagram Physics Science Stock Vector
Wie stark sich zwei Körper laut dem Gravitationsgesetz anziehen, hängt vor allem von ihren Massen und ihrer Entfernung zueinander ab. Isaac Newton hat das Gravitationsgesetz so formuliert: Die Anziehung zweier Körper aufgrund der Gravitation ist proportional zum Produkt der beiden Massen und indirekt proportional zum Quadrat ihres Abstandes.

What is Gravitation Definition, Formulas, Books ,Notes and More
Sir Isaac Newton FRS (25 December 1642 - 20 March 1726/27) was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author who was described in his time as a natural philosopher. He was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment that followed. His pioneering book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical.

Gravitation, Kraft, Newton Erde und Natur Astronomie Goruma
Isaac Newton (born December 25, 1642 [January 4, 1643, New Style], Woolsthorpe, Lincolnshire, England—died March 20 [March 31], 1727, London) English physicist and mathematician who was the culminating figure of the Scientific Revolution of the 17th century. In optics, his discovery of the composition of white light integrated the phenomena of colours into the science of light and laid the.
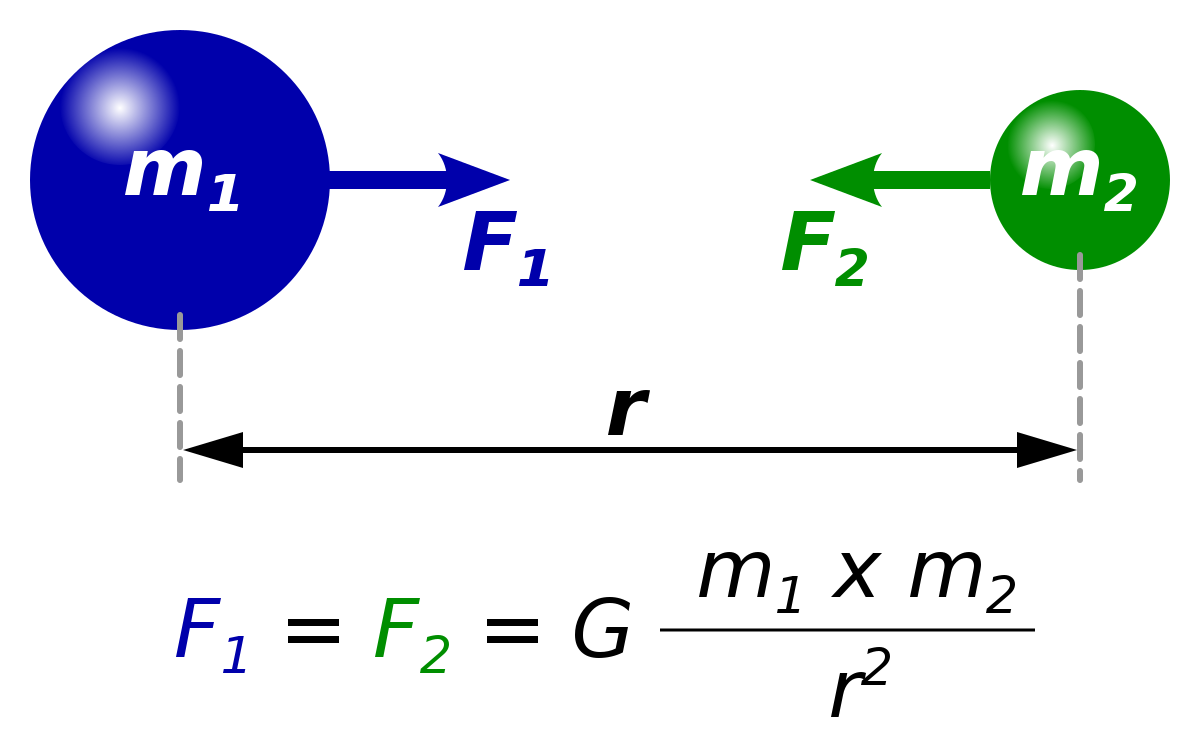
Basic Mechanics Gravity and Newton's Law of Gravitation Owlcation
Isaac Newton behauptete, dass sich alle Körper durch ihre Gravitationskraft anziehen und dass die Stärke dieser Kraft mit dem Quadrat des Abstands der Körper abnimmt.. Von der Allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie zwar inzwischen überholt, bleibt das Gravitationsgesetz doch eines der Konzepte der Physik mit der größten Tragweite, denn es.

Gravitationsgesetz • Newtonsches Gravitationsgesetz · [mit Video]
Introduction to Gravitational Fields . Sir Isaac Newton's law of universal gravitation (i.e. the law of gravity) can be restated into the form of a gravitational field, which can prove to be a useful means of looking at the situation.Instead of calculating the forces between two objects every time, we instead say that an object with mass creates a gravitational field around it.
NewtonGravitationsgesetz Gravitationskraft
The Moon's orbit has a radius of about 384,000 km (239,000 miles; approximately 60 Earth radii), and its period is 27.3 days (its synodic period, or period measured in terms of lunar phases, is about 29.5 days).Newton found the Moon's inward acceleration in its orbit to be 0.0027 metre per second per second, the same as (1/60) 2 of the acceleration of a falling object at the surface of Earth.