Study Model Educational Model Chicken Anatomy Model, Detachable Chicken
Question about chicken organs found in bird? (See photos included
The endrocrine system is made up of a number of organs and major glands located throughout the bird. These glands and organs produce a special chemical messenger called a "hormone.". Through the transport system of the chicken, the compound travels to a specific area to perform its task. [optin-monster-shortcode id.

Mystery on the underside of chicken thighs? Seasoned Advice
The anatomy of chickens is quite similar to the human anatomy in several ways, but totally different in others. Basic functions of locomotion, eating, vocalization and sexual reproduction are all similar but do have certain adaptations and differences to make it all work. We can use the chicken eye as an example.
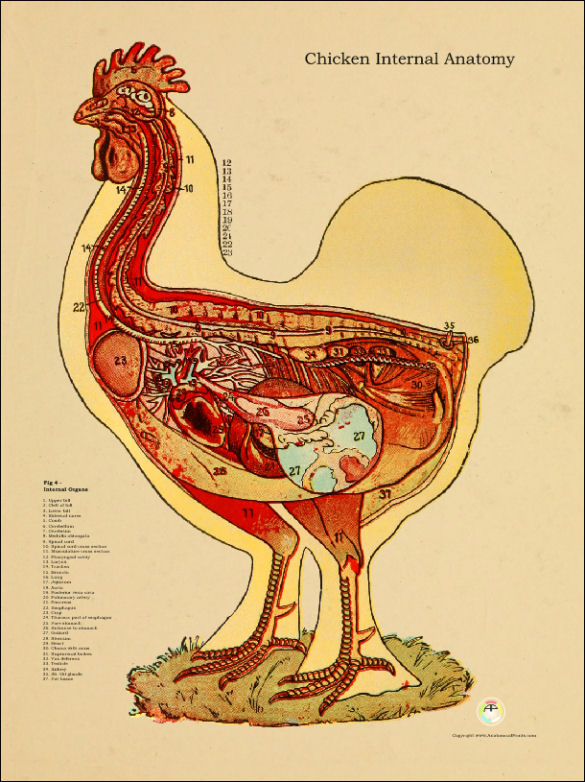
Chicken Internal Anatomical Chart
A chicken's skeleton also protects its tissues and internal organs. A chicken's skeletal system looks similar to its mammalian counterparts, although there are many crucial differences. Most of these skeletal differences between a chicken and other mammals relate to a chicken's need to be lightweight enough to fly and maintain body support.

Infographic Chicken Organs Hobby Farms
Infographic: Chicken Organs Get an inside look at your chicken's anatomy to understand what keeps it pecking around the barnyard. by Dani Yokhna. Whether you raise chickens for meat, for eggs or simply as pets, having an understanding of how your chicken's bodily systems function will make you a better chicken keeper overall. There's a.

Chicken Internal Organ System Poster Clinical Charts and Supplies
Nervous systems & important sensory organs; Reproductive system; Respiratory system & thermoregulation; Skeletal System; Evolution of the bird; Incubation; List of common anatomical and physiological terms; The Avian Egg; Backyard Poultry. Chicken coops; Common problems and treatment methods for backyard chickens; General tips for backyard.
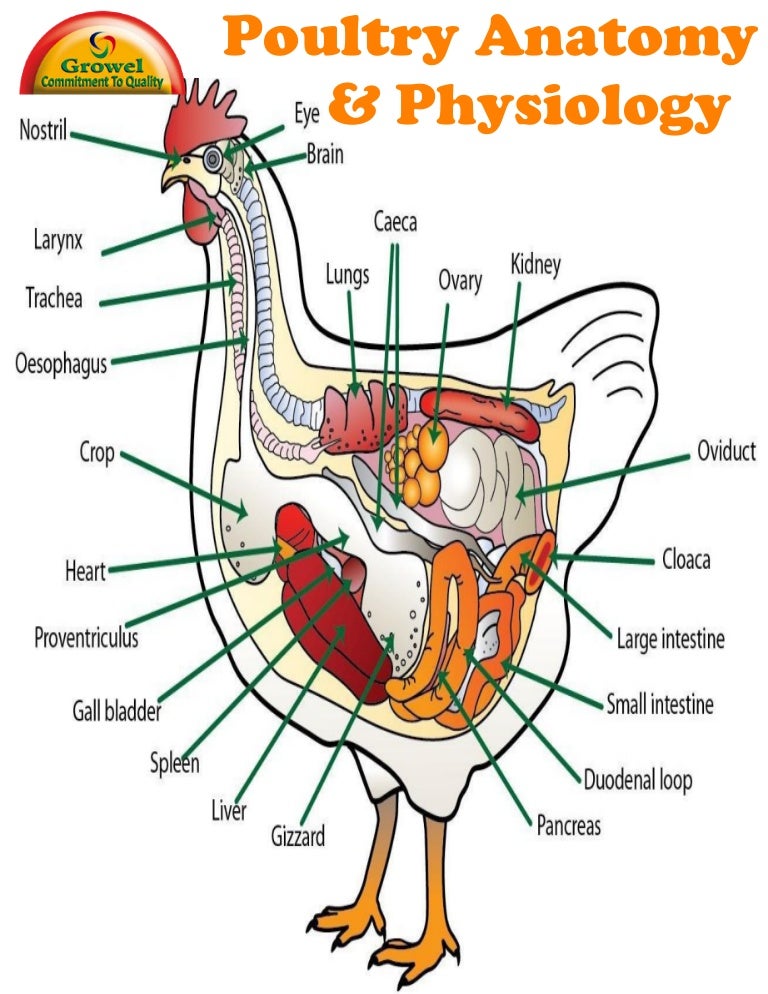
Chicken Anatomy & Physiology
The chicken's liver is a unique organ with a remarkable capacity for regeneration. In just a few weeks, the liver of a chicken may repair up to 70% of its mass. It is one of the animal kingdom's organs with the quickest regeneration rates. The liver may perform an astonishing variety of metabolic functions.
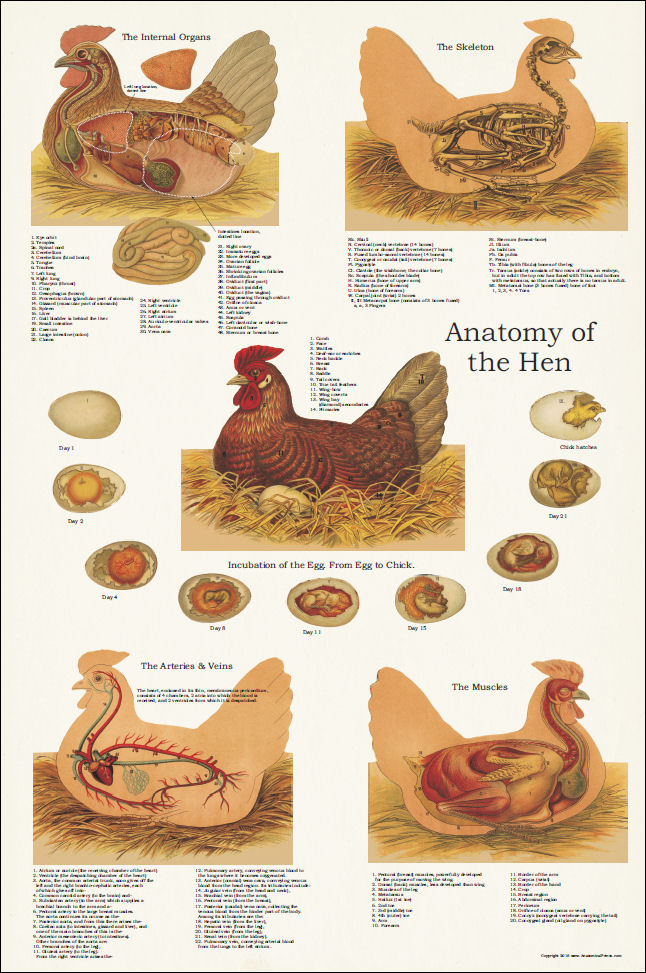
Chicken Anatomical Poster
The bones: Chicken bones are mainly made of tightly bound collagen fibers and phosphorus and calcium. About 80% of a bird's phosphorus and 99% calcium are stored in the bones and are converted into usable states by vitamin D. The egg shell becomes weak or non-existent if the chicken has a calcium deficiency.
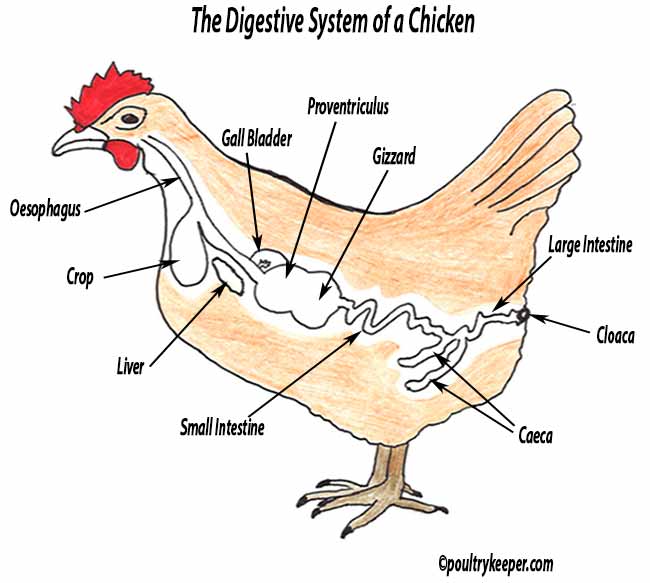
The Digestive System of a Chicken
The easiest anatomy of the chicken to assess is the external anatomy. This is the plumage and various appendages that can be seen without any further investigation necessary. This includes the plumage, legs, beak, comb, wattles, eyes, toes, tongue, mouth and skin. . Diagram 1 shows the external anatomy of a mature rooster .

Chicken Anatomy Internal Organs of Hen (A link to Everything that has
Organs of the chicken digestive system Okay, first, start with the organs of the chicken digestive system. You will find the following different organs in the chicken digestive system. Please use the chicken digestive system labeled diagram and find out all the organs from the actual sample. Mouth cavity (tongue and beak) Pharynx of chicken
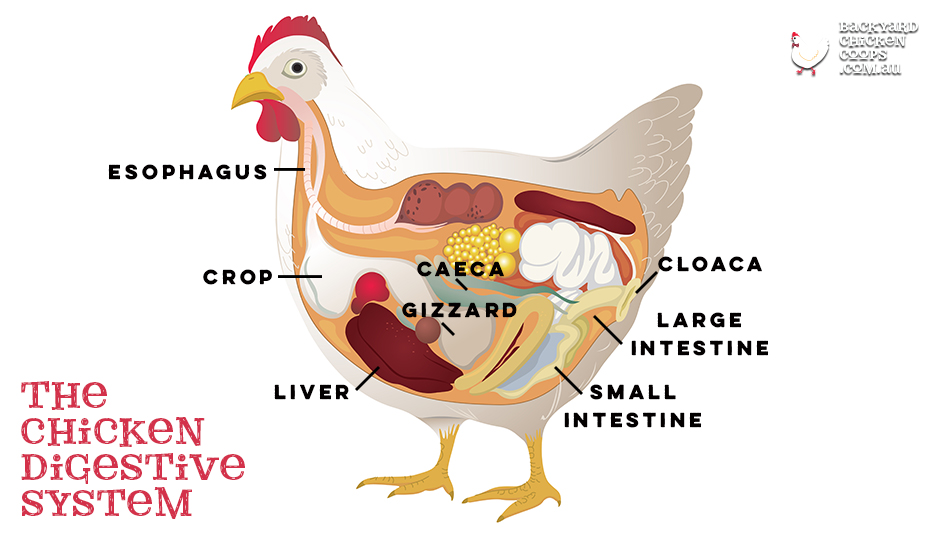
Making Sense Of Your Chickens Digestive Health
Chicken Anatomy of Bone, Legs, and Wings. Bird bones are composed mainly of calcium and phosphorus and a fine web of collagen fibers that are bound tightly together. The skeleton provides support and protection, much as the human skeleton does. 99% of calcium and 80% of phosphorus are stored in the bones.
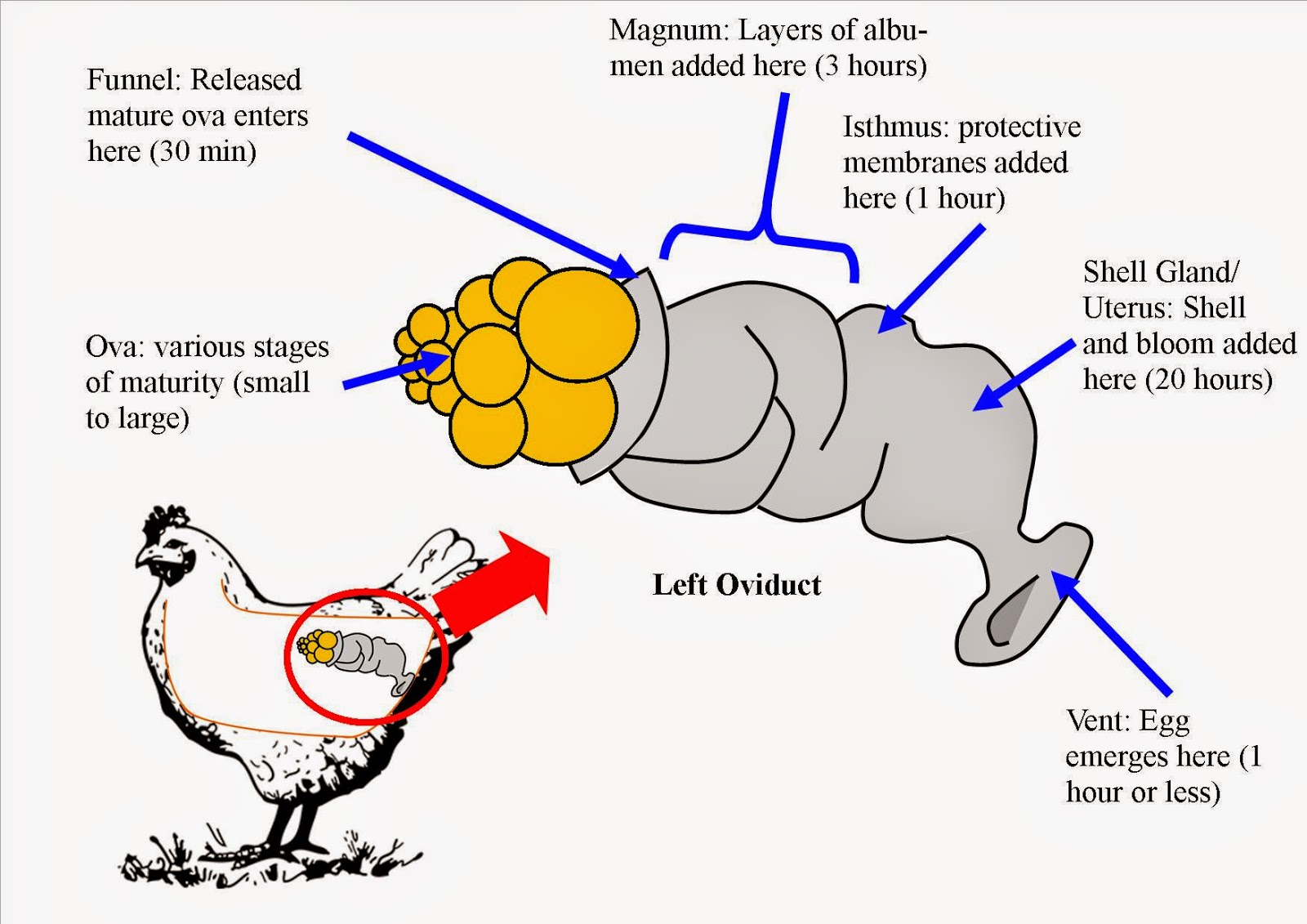
Roots 'n' Shoots The C Files How to raise chickens Layers & Nest
Chicken organs have varying nutritional profiles. The liver is rich in vitamin A, iron, and copper, making it a nutrient-dense organ. Heart contains high levels of iron, zinc, and B vitamins, promoting red blood cell formation and energy metabolism. Gizzards are a good source of protein and contain a moderate amount of iron and zinc.
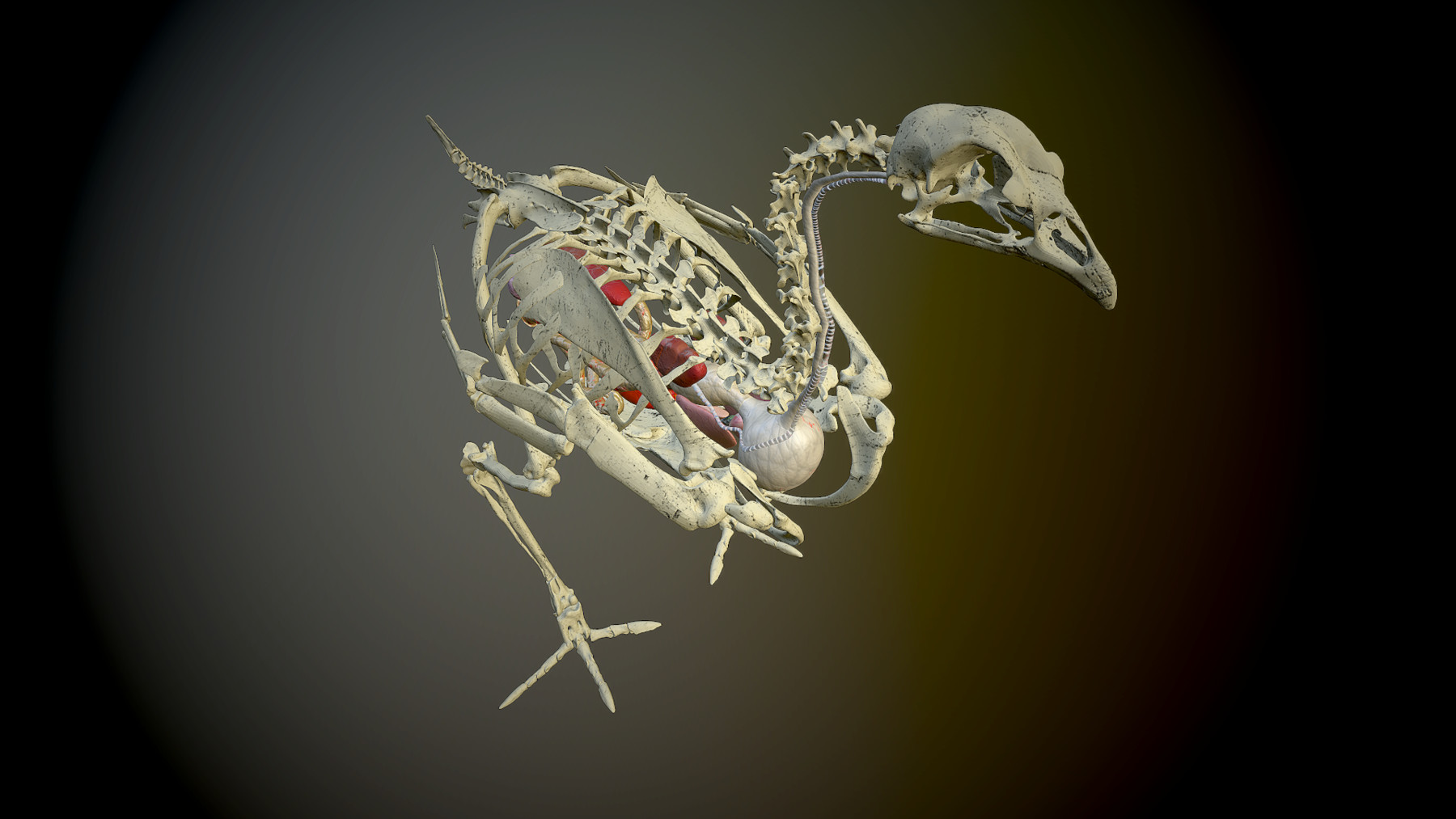
ArtStation Anatomic chicken skeleton and organs Resources
The glandular stomach of a chicken is an elongated, spindle-shaped organ that directs craniocaudally. It extends from the fourth thoracic vertebrae to the seventh thoracic vertebrae. This glandular part of the chicken stomach is the continuation of the esophagus without a clear anatomical boundary.

Study Model Educational Model Chicken Anatomy Model, Detachable Chicken
Organ meats, also known as "offal," are the consumable organs of animals. Organ meats include livers, hearts, brains, and intestines, to name a few. There are many health benefits to eating organ meats, but there are also some downsides. Which is the biggest organ of a chicken?

chicken digestive health Chicken anatomy, Poultry, Chicken cages
A chicken's head has several parts, as shown in Figure 7. One of the most prominent features on a chicken's head is the comb. Figure 8 shows different types of combs. A chicken's comb and wattles are red, soft, and warm. Chickens do not have external ears as humans do. The ears are just openings into the ear canal, and each is protected.

A Chicken's Digestive System The Journey From Feed to Egg Backyard
The chicken has a typical avian digestive system. In chickens, the digestive tract (also referred to as the gastrointestinal tract or GI tract) begins at the mouth, includes several important organs, and ends at the cloaca. Figure 1 shows a chicken digestive tract, and Figure 2 shows the location of the digestive tract in the chicken's body.

Digestive system Poultry Hub
The neck contains several important muscles and bones that allow the chicken to move its head around. Beneath the skin of the neck are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. The torso houses most of the chicken's internal organs including the heart, lungs, digestive system, and reproductive system.