Trigonometric Addition and Difference Formulas (Identities) Also double angle formulas. hubpages
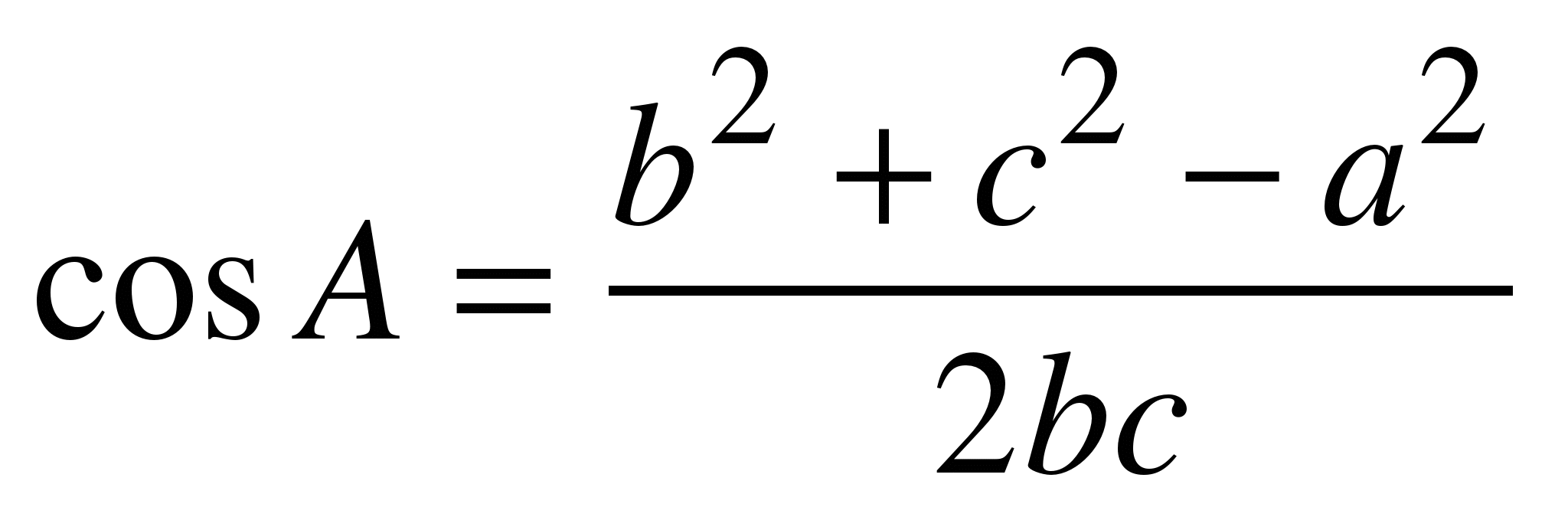
the Cosine Rule National 5 Maths
Maths Math Formula Trigonometry Formulas Trigonometry Formulas In Trigonometry, different types of problems can be solved using trigonometry formulas. These problems may include trigonometric ratios (sin, cos, tan, sec, cosec and cot), Pythagorean identities, product identities, etc.

law of cosines Law of cosine (cosine law)
Learn to derive the formula of cos (A + B). Proof of expansion of cos(A+B). cos (A +B) is an important trigonometric identity. We all learn the expansion and.

Cos (a b) Formula, Proof, Examples What is Cos(a b)?
19 I know that there is a trig identity for cos ( a + b) and an identity for cos ( 2 a), but is there an identity for cos ( a b)? cos ( a + b) = cos a cos b − sin a sin b cos ( 2 a) = cos 2 a − sin 2 a cos ( a b) =? trigonometry Share Cite asked May 8, 2014 at 22:36 TechMaster100 499 2 6 13 2
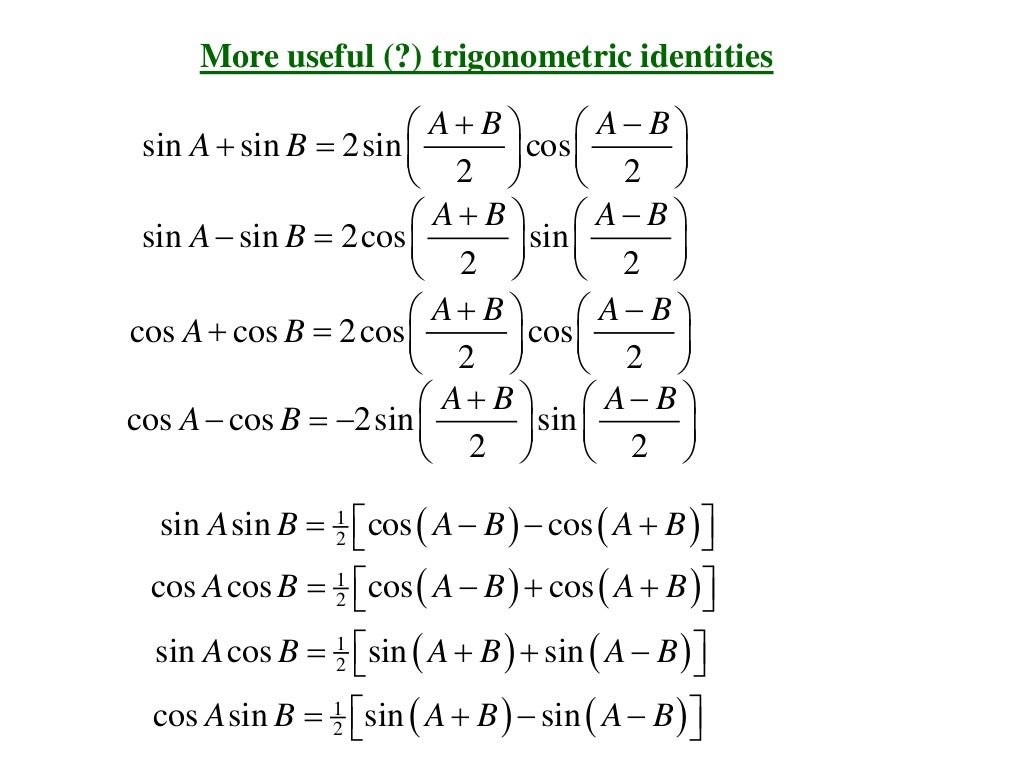
Useful trigonometric identities
Product to Sum Formulas sin x sin y = 1/2 [cos (x-y) − cos (x+y)] cos x cos y = 1/2 [cos (x-y) + cos (x+y)] sin x cos y = 1/2[sin(x+y) + sin(x−y)] cos x sin y = 1/2[sin(x+y) - sin(x−y)] Sum to Product Formulas sin x + sin y = 2 sin [ (x+y)/2] cos [ (x-y)/2] sin x - sin y = 2 cos [ (x+y)/2] sin [ (x-y)/2]
Cos A B Formula TRANSFORMACIONES TRIGONOMÉTRICAS DE SUMA A PRODUCTO Y DE Formulas for
Trigonometric Identities Purplemath What is an identity? In mathematics, an "identity" is an equation which is always true, regardless of the specific value of a given variable. An identity can be "trivially" true, such as the equation x = x or an identity can be usefully true, such as the Pythagorean Theorem's a2 + b2 = c2 MathHelp.com

Law of Cosine (Cosine Law) with Examples and Proof Teachoo
The formula of cos (a+b)cos (a-b) is given by cos (a+b)cos (a-b) = cos 2 a -sin 2 b. In this post, we will establish the formula of cos (a+b) cos (a-b). Note that cos (a+b) cos (a-b) is a product of two cosine functions. We will use the following two formulas: cos (a+b) = cos a cos b - sin a sin b. (i) cos (a-b) = cos a cos b + sin a sin b. (ii)

7 TRIGONOMETRY ( PRODUCT FORMULA SIN(A+B).SIN(AB),COS ALSO AND SOME IMPORTANT TRICK) YouTube
Formula ( 1). cos ( a + b) = cos a cos b − sin a sin b ( 2). cos ( x + y) = cos x cos y − sin x sin y Introduction Let us consider that a and b are two variables, which denote two angles. The sum of two angles is written as a + b, which is actually a compound angle.

Trigonometry
Cosines Tangents Cotangents Pythagorean theorem Calculus Trigonometric substitution Integrals ( inverse functions) Derivatives v t e In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined.

Cos A B Formula TRANSFORMACIONES TRIGONOMÉTRICAS DE SUMA A PRODUCTO Y DE Formulas for
Cos a Cos b is a trigonometric formula that is used in trigonometry. Cos a cos b formula is given by, cos a cos b = (1/2) [cos (a + b) + cos (a - b)].
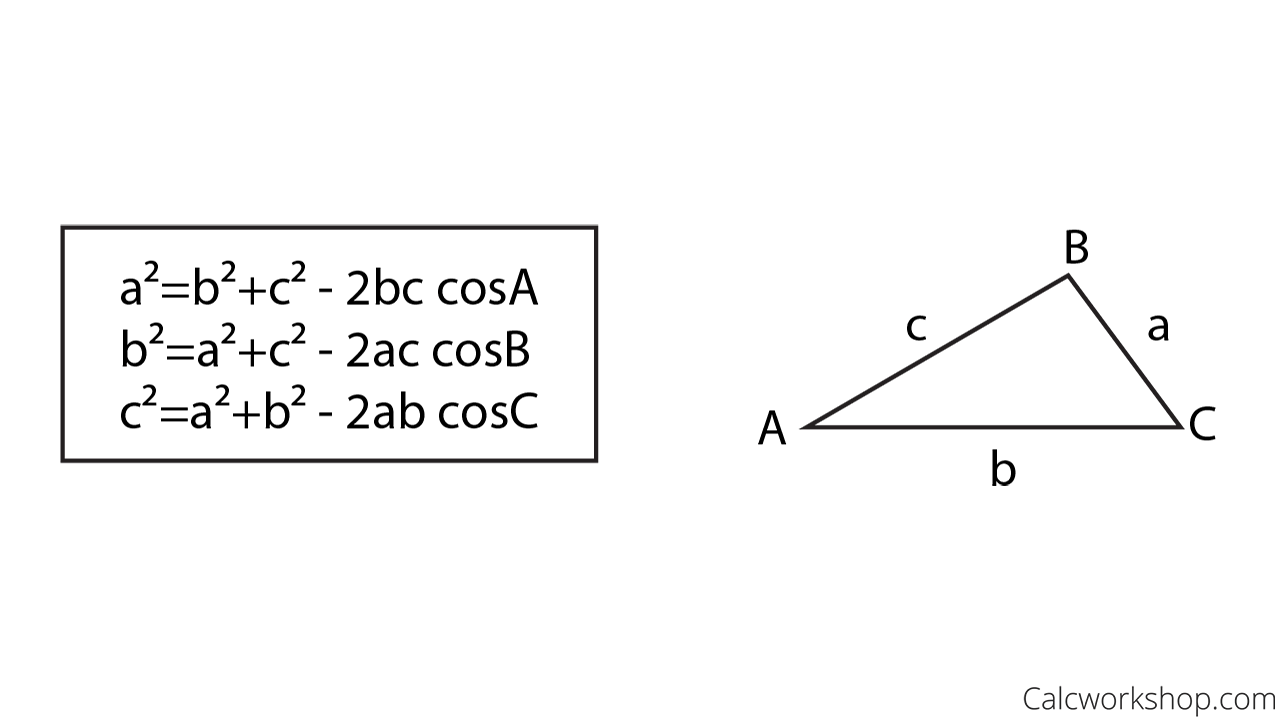
What is the Law of Cosines? (Explained in 3 Powerful Examples!)
Get Started Cos (a + b) In trigonometry, cos (a + b) is one of the important trigonometric identities involving compound angle. It is one of the trigonometry formulas and is used to find the value of the cosine trigonometric function for the sum of angles. cos (a + b) is equal to cos a cos b - sin a sin b.

Trigonometry
In trigonometry, cos (a - b) is one of the important trigonometric identities, that finds application in finding the value of the cosine trigonometric function for the difference of angles. The expansion of cos (a - b) helps in representing the cos of a compound angle in terms of trigonometric functions sine and cosine.

Cos A Cos B Cos C Communauté MCMS
In this explainer, we will learn how to use Euler's formula to prove trigonometric identities like cos(A+B)= cosA.cosB- sinA.sinBand sin(A+B)= sinA.cosB+ sin.

Law of Cosine (Cosine Law) with Examples and Proof Teachoo
The trigonometric identity Cos A - Cos B is used to represent the difference of cosine of angles A and B, Cos A - Cos B in the product form using the compound angles (A + B) and (A - B). We will study the Cos A - Cos B formula in detail in the following sections. Cos A - Cos B Difference to Product Formula
The Cosine Rule IGCSE at Mathematics Realm
The formula of cos (A + B) is cos A cos B - sin A sin B. Example : If sin A = 3 5 and cos B = 9 41, find the value of cos (A + B). Solution : We have, sin A = 3 5 and cos B = 9 41 ∴ cos A = 1 - s i n 2 A and sin B = 1 - c o s 2 B cos A = 1 - 9 25 = 4 5 and sin B = 1 - 81 1681 = 40 41 Now, By using above formula,

IDENTIDADES TRIGONOMÉTRICAS PARA LA SUMA Y RESTA DE ÁNGULOS
Because of all that we can say: sin (θ) = 1/csc (θ) cos (θ) = 1/sec (θ) tan (θ) = 1/cot (θ) And the other way around: csc (θ) = 1/sin (θ) sec (θ) = 1/cos (θ) cot (θ) = 1/tan (θ) And we also have: cot (θ) = cos (θ)/sin (θ) Pythagoras Theorem

cos(A+B) YouTube
Trigonometric Identities are useful whenever trigonometric functions are involved in an expression or an equation. Trigonometric Identities are true for every value of variables occurring on both sides of an equation. Geometrically, these identities involve certain trigonometric functions (such as sine, cosine, tangent) of one or more angles.. Sine, cosine and tangent are the primary.